In a previous articles, we discussed the discovery of wirelessly powering life-supporting medical devices within the human body thanks to wireless device engineering; a discovery that now makes wireless medical devices manufacturing possible. The impact of wireless medical devices manufacturing and engineering in medicine is the ability to create better versions of these devices. Ones that don’t require maintenance and the recharging of batteries through surgery and possibly in the future,devices that can perform internal surgery without being invasive. The key to creating such devices however is the ability to wirelessly and harmlessly transmit signals and power into the human body. Radio waves can be converted into power and can harmlessly pass through the body but the challenge to this is that radio waves dissipate within the body’s tissues.
Wireless Medical Devices Manufacturing Possibilities
Through Wireless Medical Devices Manufacturing and engineering, small devices the size of a grain of rice can be powered by amplified radio waves thanks to the wireless charging technology within them. This technology converts radio waves into electrical power. In order to receive enough radio waves to be converted to power, MIT researchers and scientists from Brigham and Women’s Hospital developed a technique wherein radio waves of various frequencies are transmitted through a network of antennas. When these frequencies mix and overlap, they can become strong enough to penetrate the tissues of the human body for the wireless device sensors to convert to energy.Therefore, these devices can theoretically be situated or can move anywhere in the human body.

While not powerful enough to power artificial hearts, the technique can power small devices the size of a grain of rice but the researchers envision that these devices can become smaller. Power is the same hurdle that keeps medical nanotechnology in the design stage. Bu thanks to this power transmission technique, these devices can or will be able to:
- Directly deliver medicine in certain areas where they’re needed
- Stimulate the brain with electricity or light
- Send probes to target areas without invasive endoscopy
- Possibly destroy cancer cells directly without radiology and chemo-therapy or possibly apply targeted chemo-therapy as in the first item.
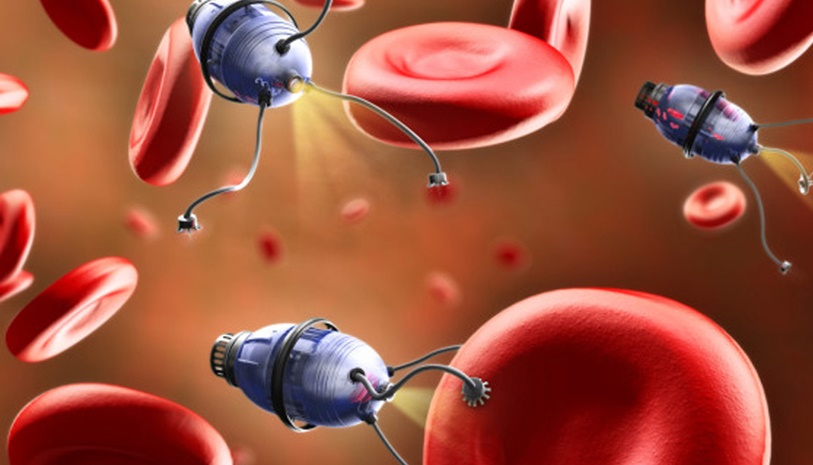
This science to power in-power devices is no longer theoretical as it has already been tested on pigs with implanted devices. These devices can receive power within ten centimeters deep inside bodily tissue while the radio transmitters were situated within one meter outside the body for that to be possible. The closer the sensors get to the outside of the body, the location of the transmitters become exponential up to 38 meters away. So currently, there is a limit to how deep within the body the devices can go because the devices would have to have transmitters of their own to transmit signals back to the outside antennae. It won’t be long however until the researchers will be able to transmit and receive signals powerful enough to power the devices anywhere within the body. It shouldn’t be long until the technology of wireless medical devices manufacturing becomes mature enough to power not only small or nanotech medical devices but full-blown artificial organs or organ support devices as well. And that’s from anywhere within the house or workplace.
Giltronics Associates Inc, a Printed Circuit board Assembly & EMS Company based in Los Angeles works and helps their clients to developing and manufacturing in the Smart Systems industry. You can reach Giltronics Team by calling them directly at +tel:+180084656331-800-846-5633 or emailing by clicking here.
